Knock knees refers to the condition where the knees are tilted to the inside and touch eachother while the ankles remain spaced out.
Knocked knees are medically known as genu valgum.
This article will discuss the signs, causes, and different treatments for knock knees in children.
Are knock knees in children normal?
Knock knees are normal at certain points during childhood but these do correct as the child grows.
At the points where it’s normal, it’s called physiological or normal, that is physiological genu valgum.
Typically, this is what is normal based on age.
- 0 to 2yrs; bowed knees, also known as genu varum
- 3 to 6yrs; Knock knees (topic under discussion)
- 7 years and above; straight legs.
Do you want to see a paediatric orthopaedic surgeon?
Signs of knock knees
- The knees touch
- Space between the ankles
- Outward facing feet
When should a parent be concerned about knock knees?
- If knock knees persist beyond 6 years
- Asymmetry of the knees. If one knee is more knocked than the other
- If there is pain in the knees and hips.
- Worsening of the knock knees over time, especially after the age of 5yrs.
Other causes of knock knees in children
- Metabolic diseases like Rickets. These are conditions that disrupt the vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate levels in the body.
- Malunion of bones. If a bone is aligned wrongly when it breaks, it could lead to knock knees
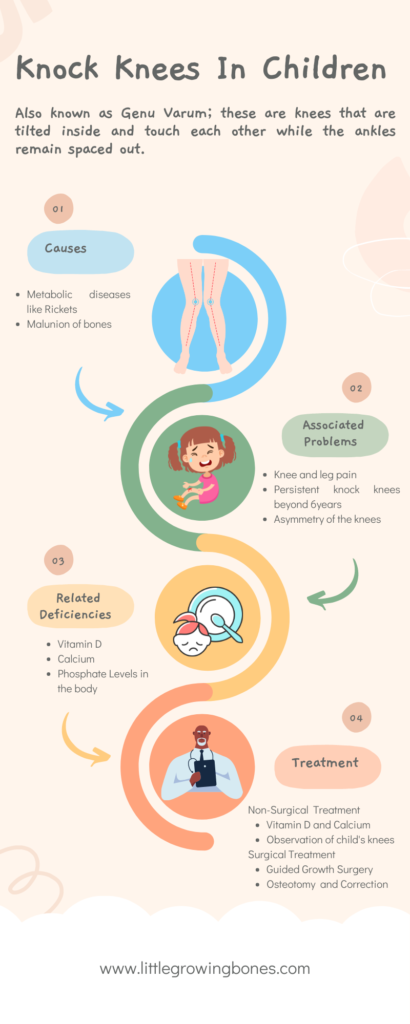
Treatment of knock knees
The treatment for Knock knees is based on the cause. The treatment is divided into surgical and nonsurgical treatment.
Nonsurgical treatment
- Vitamin D and calcium supplements.
These are used if the child is identified to have a deficiency in any of these micronutrients.
- Observation.
Observation of the child’s knees as he/she grows especially for physiological genu valgum.
Surgical treatment
There are two types of surgery that can be done.
Guided growth surgery
This is also referred to as 8plate surgery or hemiepiphysiodesis.
It is done in children who are still growing and takes advantage of their potential to grow to correct the deformity.
Little plates and screws are surgically placed adjacent to the side of the growth plate where the deformity is and then they are surgically removed after the deformity has corrected.
Osteotomy and correction
Osteotomy refers to the cutting of bone. In this case, the bone is cut and aligned in the right position and then held in place with an orthopedic implant.
In conclusion, Knock knees or genu valgum is a common condition in children. It can also be part of normal growth or a sign of abnormality in the bones. For most children, it corrects as they grow however if it fails, it can be treated.