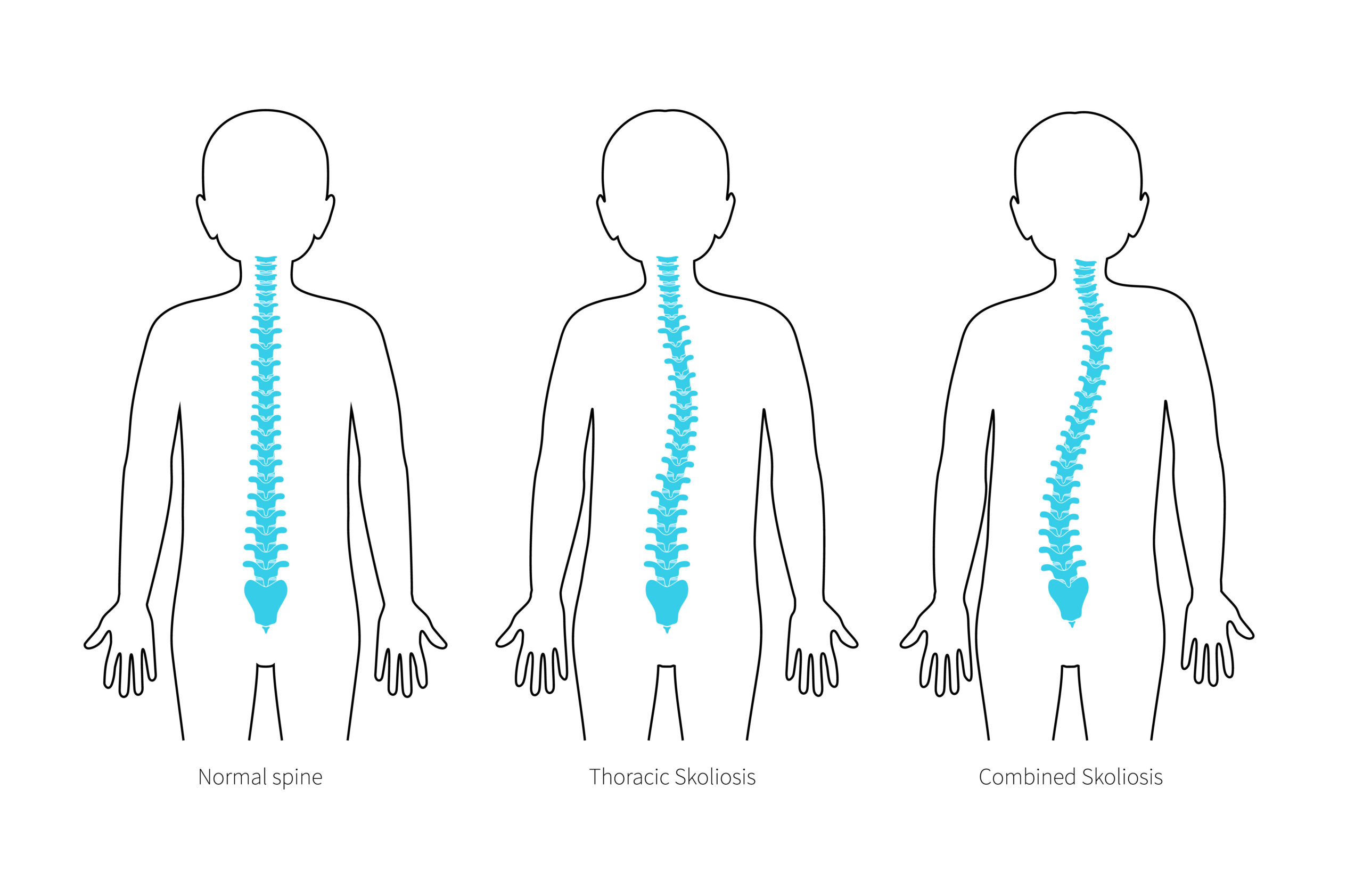
Scoliosis is the lateral curvature of the spine (backbone). If a curve is more than 10 degrees, then it is termed scoliosis.
Scoliosis is commonly classified into three types;
- Congenital type
The congenital type arises because of an inborn defect in the bones of the back.
- Neuromuscular type
The neuromuscular type problem stems from a problem in the spinal cord or muscular problems.
- Idiopathic type.
The most common type is idiopathic scoliosis whose cause is not known. Idiopathic type is further divided into infantile type, juvenile type, and adolescent type.
This article will mostly revolve around idiopathic scoliosis.
Scoliosis will be termed as is, depending on the region on the back where the biggest curve is; for example, thoracic scoliosis is the curve is in the thoracic spine or lumbar scoliosis etcetera.
Who gets idiopathic scoliosis?
Both girls and boys are affected equally but the bigger curves will commonly be seen in girls. Presentation often coincides with the years of adolescence when the body is going through rapid change. This leaves many girls very self-conscious about their body images.
Signs and symptoms of Scoliosis
- Most children with scoliosis will be noticed first by their family members and playmates.
- An obvious hump on the back
- Unevenness of the shoulder blade
- Pelvic obliquity. One hip may appear higher than the other.
Sometimes, the legs may appear unequal which may cause a limp while walking.
- Neurological symptoms.
These include pins and needles in the hands or feet. Weakness and abnormal sensation in the extremities. The presence of neurological symptoms is one that doctors need to pay attention to.
Do you need to see a paediatric orthopaedic surgeon?
Should I be worried if I am diagnosed with idiopathic scoliosis?
A scoliosis curve has to be quite large to cause major health issues. So aside from the aesthetics, most scoliosis curves shouldn’t cause any alarm.
In most children, the scoliosis curve sill stop increasing once they have attained skeletal maturity, so no there is no need to worry.
Achieving skeletal maturity means that your bones can no longer grow any taller because the growth plates have closed off.
But don’t stop seeing your doctor altogether. Endeavor to show up for appointments to check for curve progression.
For large curves, however (that is those 80 to 100 degrees) there is a need for frequent review as big scoliosis curves have been noted to be associated with pulmonary (breathing) disturbances.
Treatment for scoliosis
Treatment is divided into 3 types. Different treatments will be employed depending on your curve magnitude.
- Observation
Here your doctor will observe the progression of your backbone curve without much intervention
- Bracing
The doctor will prescribe a brace that should be worn based on the doctor’s prescription. The brace will not treat scoliosis but may help reduce the progression of the curve.
- Surgery
Surgery is recommended for patients with large curves and those that are associated with cardiac and pulmonary compromise.
In conclusion, scoliosis is a medical term for lateral curvature of the spine. its broadly divided into congenital, neuromuscular, and idiopathic. idiopathic type is the most common and is treated when it becomes symptomatic.